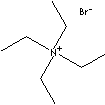| CAS
NO. |
71-91-0 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
200-769-4 |
| FORMULA |
(C2H5)4NBr |
| MOL
WT. |
210.16 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2923.90 |
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
TEAB; Tetrylammonium bromide; |
| Ethanaminium, N,N,N-triethyl-, bromide; Bromure de tetraethylammonium;
TEA; Tetraethylammnonium bromide; ETAMBRO;
|
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
White to off white crystalline
powder |
|
MELTING
POINT
|
285
- 287 C (Decomposes) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.4 |
|
SOLUBILITY
IN WATER
|
Very
soluble |
|
pH
|
6.5 (In solution) |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
5.3 |
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
Not expected to be a fire hazard |
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions (Hygroscopic)
|
|
APPLICATIONS
|
Quaternary ammonium compounds are any of a group of ammonium salts in which
organic radicals have been substituted for all four hydrogens of the original
ammonium cation. They has a central nitrogen atom which is joined to four
organic radicals and one acid radical. The organic radicals may be alkyl, aryl,
or aralkyl, and the nitrogen can be part of a ring system. They are prepared by
treatment of an amine with an alkylating agent. They show a variety of physical,
chemical, and biological properties and most compounds are soluble in water and
strong electrolytes. In addition to their tendency of locating at the interface
of two phases (liquid–liquid or solid–liquid) to introduces continuity between
the two different phase, they have properties of disrupting micro-organisms'
cell processes. These compounds are used as ;
- Surface-active
agents
- Solvents
- Intermediates
- Active Ingredient for Conditioners
- Antistatic Agent
- Detergent Sanitisers
- Softner for textiles and paper
products
- Phase Transfer Catalyst
- Antimicrobials
- Disinfection Agents
And Sanitizers
- Slimicidal Agents
- Algaecide
- Emulsifying Agents
- Pigment Dispersers
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
POWDER
|
|
APPEARANCE
|
White to off white crystalline
powder |
| ASSAY |
99.0%
|
|
FREE
AMINE
|
0.5%
max
|
|
ASH
|
0.5%
max
|
|
MOISTURE
|
0.5%
max
|
|
50%
SOLUTION
|
|
APPEARANCE
|
Clear
to pale yellow
liquid |
|
ASSAY |
50.0%
min
|
|
FREE
AMINE
|
1.0%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
Not regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF PHASE TRANSFER CATALYSIS
|
|
'Phase transfer catalysis (PTC)' methodology is a powerful tool improving
process efficiency, product selectivity and providing mild reaction conditions
in organic chemical reactions. In many chemical reaction situations, there are
different species (immiscible liquids or solid and liquid) which don't react
each other due to separation by an interface. Small quantity of 'phase-transfer
catalyst', involves a substrate (soluble in the organic layer) and an anionic
reagent or a nucleophile (dissolved in the aqueous layer), extracts one of the
reactants, most commonly an anion, across the interface into the other phase
where reaction can take place with the substrate and reaction can proceed. The
quaternary ammonium salts can carry the nucleophile from the aqueous to organic
phase and are used as the most commonly used as 'phase-transfer catalyst'. The
phosphonium derivatives favoring higher thermal stability property are also
used. Crown ethers and polyethylenglycol compounds are also widely used in this
application. |